Consensus problems, where a group of agents, such as unmanned vehicles, machines, or robots, need to agree on certain variables only through local communication within themselves, have attracted considerable attention as a fundamental issue in cooperative control of multi-agent systems. Simply put, a multi-agent system comprises multiple decision-making agents that interact among themselves in a common environment to achieve common or conflicting goals depending on the situation.
Depending on whether agents track a predetermined leader, these problems can be classified into leaderless or leader-following consensus. Researchers have extensively studied both types of problems and developed consensus protocols. However, most current protocols only provide asymptotic consensus.
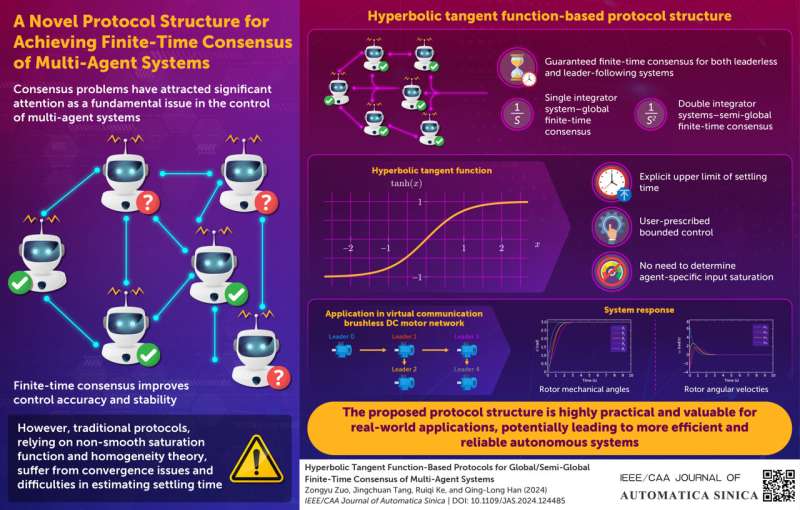
Some applications require exact consensus in a limited time or finite-time consensus. Achieving such a consensus results in improved control accuracy and stability. In practical applications, finite-time consensus requires considerable control effort. However, there are physical limitations to control effort, which if neglected, can degrade controller performance.
Studies have explored solutions for finite-time control methods subject to constraints, but most methods rely on homogeneity theory, in which ensuring convergence of consensus is difficult, and an exact settling time is hard to estimate.
Addressing these issues, a team of researchers, including Professor Zongyu Zuo, Mr. Jingchuan Tan, and Mr. Ruiqi Ke, all from Beihang University, China, and IEEE Fellow Professor Qing-Long Han from Swinburne University of Technology, Australia, developed a novel protocol structure for achieving global and semi-global finite-time consensus for both leaderless and leader-following multi-agent systems. Their study was published in the IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica.
The team was motivated by a fascination with the potential of robotic systems and artificial intelligence to transform our daily lives and tackle complex societal challenges efficiently and sustainably. Prof. Zuo intuitively explains their work, “Imagine a group of dancers who need to perform a synchronized routine, without directly seeing each other, only following cues from those nearby. Our work is akin to creating a set of rules that helps these dancers synchronize perfectly in a short time, ensuring everyone performs beautifully together even if they have limitations in how quickly they can move.”
The protocols presented in the study use a hyperbolic tangent function, instead of the non-smooth saturation function used in traditional protocols. These protocols guarantee global and semi-global finite-time consensus for integrator and double integrator type systems, respectively. Moreover, they also allow explicit calculation of an upper limit for settling time and a user-prescribed bounded control level for closed-loop systems, making them highly practical and valuable for real-world applications.
Additionally, unlike traditional protocols, the hyperbolic tangent function avoids the need to determine input saturation for each agent, simplifying the design and stability analysis of the protocols. The researchers demonstrated the effectiveness of the new protocol structure through illustrative examples for single- and double-integrator multi-agent systems and by applying it to a practical system with multiple direct current motors.
Highlighting the practical applications of this study, Prof. Zuo says, “These protocols have broad applications, such as autonomous drone fleets for agricultural or surveillance tasks, coordinated control of robotic arms, and synchronized traffic light systems.
“Ultimately, our research could improve the efficiency and reliability of autonomous systems. For example, better traffic management systems could reduce congestion and pollution, while more coordinated disaster response robots could save lives during crises.”
Overall, the innovative protocol structure marks a significant achievement in the field of consensus problems, leading to enhanced multi-agent autonomous systems.
More information:
Zongyu Zuo et al, Hyperbolic Tangent Function-Based Protocols for Global/Semi-Global Finite-Time Consensus of Multi-Agent Systems, IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica (2024). DOI: 10.1109/JAS.2024.124485
Provided by
Chinese Association of Automation
Citation:
Study presents novel protocol structure for achieving finite-time consensus of multi-agent systems (2024, June 12)
retrieved 12 June 2024
from https://techxplore.com/news/2024-06-protocol-finite-consensus-multi-agent.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.









