Recently, the National Science Open magazine published online a review article by Professor Jiao Shuhong’s group from the University of Science and Technology of China and Professor Cheng Tao’s team from Suzhou University. The review discussed the preliminary application and huge development potential of artificial intelligence (AI) technology in battery interface research.
This review starts from a novel perspective of the critical role of electrolyte chemistry and electrode interface on the performance and safety of lithium batteries and highlights the application prospects of machine learning models in this research field.
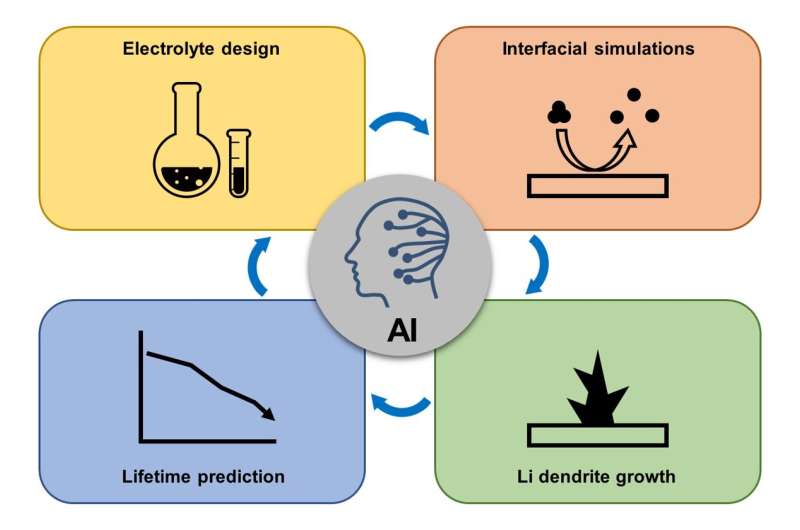
First, the AI methods and models used in battery research are introduced, and the current applications of AI in electrolyte design, interface formation mechanisms and characterizations, lithium dendrite growth and inhibition, and battery performance degradation and life prediction are outlined.
In view of the limitations of traditional experimental techniques, this review proposes that by combining experiments and simulations, an in-depth understanding of the formation process and characteristics of the battery interface at the molecular level can be gained. AI can also be used to extract key descriptors from large data sets and provide new insights for the development of more efficient, safer, and longer-lasting battery systems.
AI or machine learning models have great potential as powerful tools in future battery research, and this review further highlights the importance of developing this technology within the battery science community.
More information:
Yawei Chen et al, Artificial intelligence for the understanding of electrolyte chemistry and electrode interface in lithium battery, National Science Open (2023). DOI: 10.1360/nso/20230039
Science China Press
Citation:
Artificial intelligence advances electrolyte design, understanding of battery interface mechanisms (2024, March 6)
retrieved 6 March 2024
from https://techxplore.com/news/2024-03-artificial-intelligence-advances-electrolyte-battery.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.









