A machine-learning algorithm demonstrated the capability to process data that exceeds a computer’s available memory by identifying a massive data set’s key features and dividing them into manageable batches that don’t choke computer hardware. Developed at Los Alamos National Laboratory, the algorithm set a world record for factorizing huge data sets during a test run on Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Summit, the world’s fifth-fastest supercomputer.
Equally efficient on laptops and supercomputers, the highly scalable algorithm solves hardware bottlenecks that prevent processing information from data-rich applications in cancer research, satellite imagery, social media networks, national security science and earthquake research, to name just a few.
“We developed an ‘out-of-memory’ implementation of the non-negative matrix factorization method that allows you to factorize larger data sets than previously possible on a given hardware,” said Ismael Boureima, a computational physicist at Los Alamos National Laboratory. Boureima is first author of the paper in The Journal of Supercomputing on the record-breaking algorithm.
“Our implementation simply breaks down the big data into smaller units that can be processed with the available resources. Consequently, it’s a useful tool for keeping up with exponentially growing data sets.”
“Traditional data analysis demands that data fit within memory constraints. Our approach challenges this notion,” said Manish Bhattarai, a machine learning scientist at Los Alamos and co-author of the paper.
“We have introduced an out-of-memory solution. When the data volume exceeds the available memory, our algorithm breaks it down into smaller segments. It processes these segments one at a time, cycling them in and out of the memory. This technique equips us with the unique ability to manage and analyze extremely large data sets efficiently.”
The distributed algorithm for modern and heterogeneous high-performance computer systems can be useful on hardware as small as a desktop computer, or as large and complex as Chicoma, Summit or the upcoming Venado supercomputers, Boureima said.
“The question is no longer whether it is possible to factorize a larger matrix, rather how long is the factorization going to take,” Boureima said.
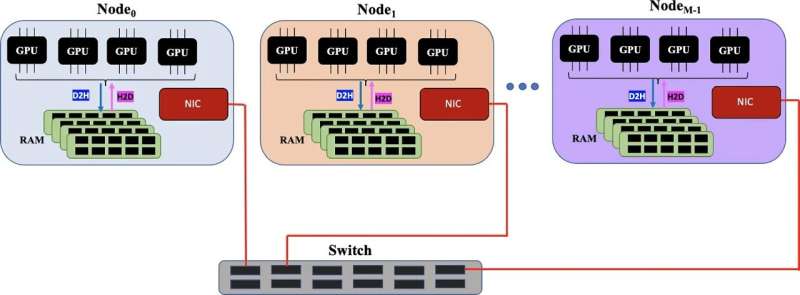
The Los Alamos implementation takes advantage of hardware features such as GPUs to accelerate computation and fast interconnect to efficiently move data between computers. At the same time, the algorithm efficiently gets multiple tasks done simultaneously.
Non-negative matrix factorization is another installment of the high-performance algorithms developed under the SmartTensors project at Los Alamos.
In machine learning, non-negative matrix factorization can be used as a form of unsupervised learning to pull meaning from data, Boureima said. “That’s very important for machine learning and data analytics because the algorithm can identify explainable latent features in the data that have a particular meaning to the user.”
The record-breaking run
In the record-breaking run by the Los Alamos team, the algorithm processed a 340-terabyte dense matrix and an 11-exabyte sparse matrix, using 25,000 GPUs.
“We’re reaching exabyte factorization, which no one else has done, to our knowledge,” said Boian Alexandrov, a co-author of the new paper and a theoretical physicist at Los Alamos who led the team that developed the SmartTensors artificial intelligence platform.
Decomposing or factoring data is a specialized data-mining technique aimed at extracting pertinent information, simplifying the data into understandable formats.
Bhattarai further emphasized the scalability of their algorithm, remarking, “In contrast, conventional methods often grapple with bottlenecks, mainly due to the lag in data transfer between a computer’s processors and its memory.”
“We also showed you don’t necessarily need big computers,” Boureima said. “Scaling to 25,000 GPUs is great if you can afford it, but our algorithm will be useful on desktop computers for something you couldn’t process before.”
More information:
Ismael Boureima et al, Distributed out-of-memory NMF on CPU/GPU architectures, The Journal of Supercomputing (2023). DOI: 10.1007/s11227-023-05587-4
Los Alamos National Laboratory
Citation:
Machine learning masters massive data sets: Algorithm breaks the exabyte barrier (2023, September 11)
retrieved 11 September 2023
from https://techxplore.com/news/2023-09-machine-masters-massive-algorithm-exabyte.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.









