In a time when the Internet has become the main source of information for many people, the credibility of online content and its sources has reached a critical tipping point. This concern is intensified by the proliferation of generative artificial intelligence (AI) applications such as ChatGPT and Google Bard.
Unlike traditional platforms such as Wikipedia, which are based on human-generated and curated content, these AI-driven systems generate content autonomously—often with errors. A recently published study, jointly conducted by researchers from the Mainz University of Applied Sciences and Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU), is dedicated to the question of how users perceive the credibility of human-generated and AI-generated content in different user interfaces. More than 600 English-speaking participants took part in the study.
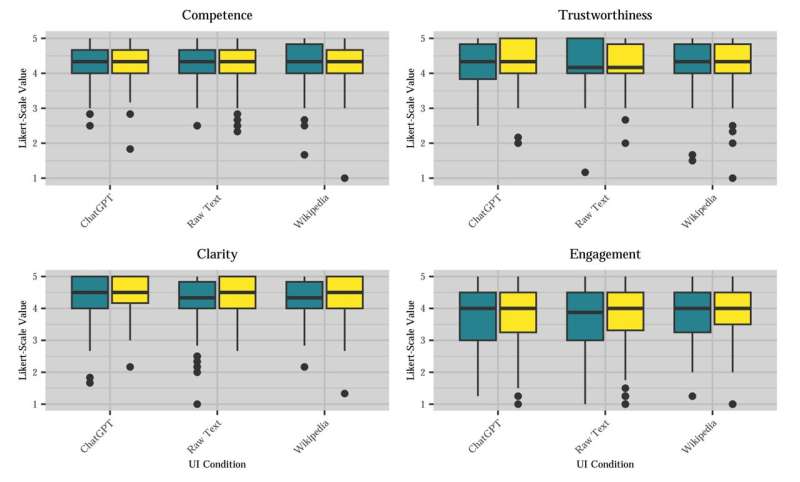
As Professor Martin Huschens, Professor for Information Systems at the Mainz University of Applied Sciences and one of the study’s authors, emphasized, “Our study revealed some really surprising findings. It showed that participants in our study rated AI-generated and human-generated content as similarly credible, regardless of the user interface.”
He added, “What is even more fascinating is that participants rated AI-generated content as having higher clarity and appeal, although there were no significant differences in terms of perceived message authority and trustworthiness—even though AI-generated content still has a high risk of error, misunderstanding, and hallucinatory behavior.”
The study sheds light on the current state of perception and use of AI-generated content and the associated risks. In the digital age, where information is readily available, users must apply discernment and critical thinking. The balance between the convenience of AI-driven applications and responsible information use is crucial. As AI-generated content becomes more widespread, users must remain aware of the limitations and inherent biases in these systems.
Professor Franz Rothlauf, Professor of Information Systems at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, added, “The study results show that—in the age of ChatGPT—we are no longer able to distinguish between human and machine language and text production. However, since AI does not ‘know,’ but relies on statistical guessing, we will need mandatory labeling of machine-generated knowledge in the future. Otherwise, truth and fiction will blur, and people cannot tell the difference.”
It remains a task of science communication and, not least, a social and political challenge to sensitize users to the responsible use of AI-generated content.
The study is published on the arXiv preprint server.
More information:
Martin Huschens et al, Do You Trust ChatGPT?—Perceived Credibility of Human and AI-Generated Content, arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2309.02524
arXiv
Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz
Citation:
AI- and human-generated online content are considered similarly credible, finds study (2023, November 29)
retrieved 29 November 2023
from https://techxplore.com/news/2023-11-ai-human-generated-online-content-similarly.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.









