Researchers from the University of Oxford have made a significant advance toward ensuring that information produced by generative artificial intelligence (AI) is robust and reliable.
In a new study published in Nature, they demonstrate a novel method to detect when a large language model (LLM) is likely to “hallucinate” (i.e., invent facts that sound plausible but are imaginary).
This advance could open up new ways to deploy LLMs in situations where “careless errors” are costly such as legal or medical question-answering.
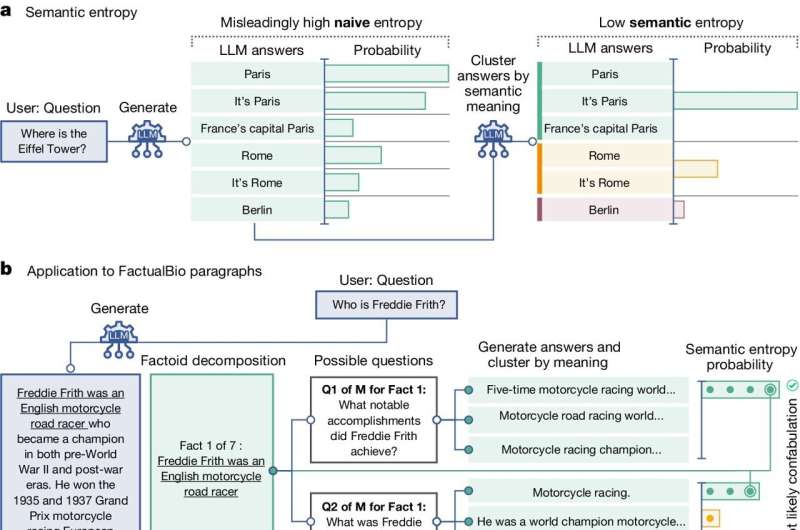
The researchers focused on hallucinations where LLMs give different answers each time it is asked a question—even if the wording is identical—known as confabulating.
“LLMs are highly capable of saying the same thing in many different ways, which can make it difficult to tell when they are certain about an answer and when they are literally just making something up,” said study author Dr. Sebastian Farquhar, from the University of Oxford’s Department of Computer Science.
“With previous approaches, it wasn’t possible to tell the difference between a model being uncertain about what to say versus being uncertain about how to say it. But our new method overcomes this.”
To do this, the research team developed a method grounded in statistics and using methods that estimate uncertainty based on the amount of variation (measured as entropy) between multiple outputs.
Their approach computes uncertainty at the level of meaning rather than sequences of words, i.e., it spots when LLMs are uncertain about the actual meaning of an answer, not just the phrasing. To do this, the probabilities produced by the LLMs, which state how likely each word is to be next in a sentence, are translated into probabilities over meanings.
The new method proved much better at spotting when a question was likely to be answered incorrectly than all previous methods, when tested against six open-source LLMs (including GPT-4 and LLaMA 2).
This was the case for a wide range of different datasets including answering questions drawn from Google searches, technical biomedical questions, and mathematical word problems. The researchers even demonstrated how semantic entropy can identify specific claims in short biographies generated by ChatGPT that are likely to be incorrect.
“Our method basically estimates probabilities in meaning-space, or ‘semantic probabilities,'” said study co-author Jannik Kossen (Department of Computer Science, University of Oxford). “The appeal of this approach is that it uses the LLMs themselves to do this conversion.”
By detecting when a prompt is likely to produce a confabulation, the new method can help make users of generative AI aware when the answers to a question are probably unreliable, and to allow systems built on LLMs to avoid answering questions likely to cause confabulations.
A key advantage to the technique is that it works across datasets and tasks without a priori knowledge, requiring no task-specific data, and robustly generalizes to new tasks not seen before. Although it can make the process several times more computationally costly than just using a generative model directly, this is clearly justified when accuracy is paramount.
More information:
Sebastian Farquhar et al, Detecting hallucinations in large language models using semantic entropy, Nature (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07421-0
University of Oxford
Citation:
Research into ‘hallucinating’ generative models advances reliability of artificial intelligence (2024, June 20)
retrieved 20 June 2024
from https://techxplore.com/news/2024-06-hallucinating-generative-advances-reliability-artificial.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.










